Advanced mapping code
On this page
In this article, you will learn about the possibility of introducing changes to your clues using JavaScript glue code. You can perform similar actions as with property and pre-process rules but you gain greater flexibility to set up complex conditions.
The advanced mapping code is applied to the clues after property and pre-process rules.
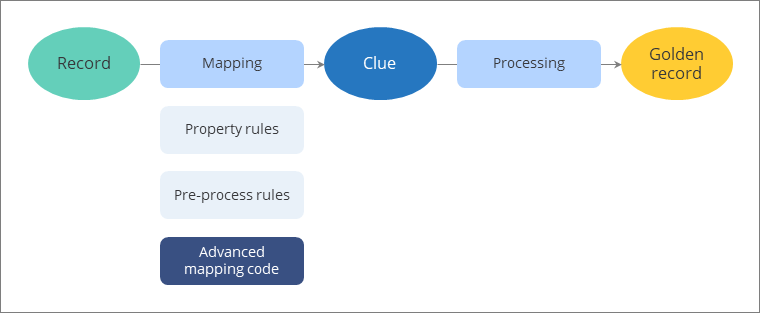
Prerequisites
To access advanced mapping, go to Administration > Feature Flags, and then turn on the Advanced Mapping feature.
Write advanced mapping code
Sometimes, the conditions in property and pre-process rules might appear cumbersome when you need to execute complex logic on your records. In such cases, you can use the advanced mapping capabilities that allow you to modify clues by executing the code. From a security perspective, advanced mapping runs on a virtual machine that does not have access to your network.
The advanced mapping code can be executed on the following levels:
-
Code mapping before sending clues – default level that allows you to modify clues using built-in methods. Our article focuses on this level because it is the most commonly used.
-
Code mapping before creating clues – additional level that only allows you to modify record values using the following code:
value['customer.companyName'] = 'Star'; [value]Where
'customer.companyName'is the name of the property,'Star'is the value that will be set to the property in each record, and[value]is an element that indicates that the code is executed for each record.
Example
Suppose you have ingested the revenue data, and you want to add tags to facilitate the retrieval of golden records in CluedIn. You want to add a tag “Golden” to those records where the revenue is greater than or equal to 1000000; and another tag “Silver” to those records where the revenue is greater than or equal to 500000 . You can achieve that by writing the advanced mapping code similar to the following example.
if (getVocabularyKeyValue('customer.revenue') >= 1000000) {
addTag('Golden');
} else if (getVocabularyKeyValue('customer.revenue') >= 500000) {
addTag('Silver');
}
[value]
[value] is an important element that indicates that the code is executed for each clue.
To modify clues by writing the advanced mapping code
-
On the navigation pane, go to Integrations > Data Sources. Then, find and open the data set.
-
Go to the Map tab, and then select Advanced.
-
In the upper-right corner, make sure that Code mapping before sending clues is selected.
-
Select Run to load all clues that were created from the data set.
The clues appear on the right side of the page. If you have created property or pre-processed rules, note that they have already been applied to the clues.
-
On the left side of the page, write the code to modify the clues as needed. You can write any JavaScript code.
To check if the code is applied as intended, select Run.
-
If you are satisfied with the result, select Save.
Your changes to the clues are saved. The advanced mapping code is executed right before you send the data into processing pipeline.
Available methods
This is a reference section that lists all available methods that you can use to write the advanced mapping code. Please refer to CluedIn Expression Language (C.E.L.) for all string and math methods. This section is focused on built-in CluedIn-specific methods.
getVocabularyKeyValue
Retrieves the clues that have a specific vocabulary key in order to apply further actions on the values or clues. In the following example, the code retrieves specific values of 'customer.industry' and adds a tag “Golden Oil & Gas” to those clues where 'customer.revenue' is greater than 750000.
if (
(getVocabularyKeyValue('customer.industry') === 'Natural Gas Distribution' ||
getVocabularyKeyValue('customer.industry') === 'Oil & Gas Production') &&
getVocabularyKeyValue('customer.revenue') > 750000
) {
addTag('Golden Oil & Gas');
}
[value]
setVocabularyKeyValue
Changes the vocabulary key values. In the following example, the code retrieves the current value of 'customer.industry' using getVocabularyKeyValue, converts it to lowercase using toLowerCase(), and then sets the updated lowercase value using setVocabularyKeyValue.
setVocabularyKeyValue('customer.industry', getVocabularyKeyValue('customer.industry').toLowerCase());
[value]
getEntityProperty
Retrieves the clues that have a specific entity property in order to apply further actions on the values or clues. In the following example, the code takes the 'name' property from the clue, converts it to uppercase using toUpperCase(), and then sets the result as the value of the 'description' property for the clue.
const name = getEntityProperty('name');
setEntityProperty('description', name.toUpperCase());
[value]
setEntityProperty
Adds or changes the value of the entity property, such as name, description, entityType, date created, and so on. In the following example, the code checks if the 'customer.industry' vocabulary key is set to 'Precious Metals', and if it is, the code sets the 'description' property of the clue to the specified string.
if (getVocabularyKeyValue('customer.industry') === 'Precious Metals') {
setEntityProperty('description', 'This record comes from corporate CRM');
}
[value]
removeVocabularyKey
Removes vocabulary key from the clues. In the following example, the code removes the 'customer.revenue' vocabulary key from all clues.
removeVocabularyKey('customer.revenue')
[value]
quarantine
Send the clues that do not meet certain conditions to quarantine. In the following example, the code checks if the value of 'customer.revenue' is absent or equal to 0. If it is, the code send such clues to quarantine.
const customerRevenue = getVocabularyKeyValue('customer.revenue');
if (customerRevenue === undefined || customerRevenue === null || customerRevenue === 0) {
quarantine();
}
[value]
addAlias
Adds aliases to the clues. In the following example, the code adds an alias taken from the 'customer.company' vocabulary key to each clue.
addAlias(getVocabularyKeyValue('customer.company'));
[value]
addTag
Adds tags to the clues. In the following example, the code checks if the value of 'customer.industry' is equal to “Oil & Gas”. If the condition is true, a tag “Oil & Gas” is added to the corresponding clues.
if (getVocabularyKeyValue('customer.industry') === 'Oil & Gas') {
addTag('Oil & Gas');
}
[value]
addCode
Adds an identifier (previously known as code) to the clue. The identifier usually consists of a business domain (previously known as entity type), an origin, and a specific value. You can specify the required origin and value to generate the code.
In the following example, the first parameter is the origin and the second parameter is the value. The resulting code would be "/Customer#myOrigin:myCode".
addCode("myCode","myOrigin")
[value]
removeTags
Removes all tags from the clue.
removeTags()
[value]
removeCodes
Removes all codes from the Codes section of the clue.
removeCodes()
[value]
removeAliases
Removes all aliases from the clue.
removeAliases()
[value]
fillVocabularyKeysIfBlank
By default, CluedIn ignores vocabulary keys that have empty values during ingestion. This means such keys will not be written to the entity unless explicitly handled.
The fillVocabularyKeysIfBlank() method allows you to populate these empty vocabulary keys with a zero-width space character (\u200B) when passed as a parameter. This makes them visually appear blank while still ensuring the keys exist in the entity. It is useful when downstream processes, such as mapping rules or deduplication, rely on the presence of those keys.
fillVocabularyKeysIfBlank("\u200B");
[value]
In the above example, all empty vocabulary keys are assigned a zero-width space. This allows them to be treated as non-empty during rule evaluation or processing.
Use case example
Suppose you have a data source where certain fields (such as customer.email or customer.phoneNumber) must be intentionally cleared to comply with privacy regulations like GDPR or CCPA. By default, CluedIn ignores empty values during ingestion, which means the existing values in the golden record are retained. The following script ensures that the target vocabulary keys are explicitly updated with blank values instead :
Note: The zero-width space will not be visible in the CluedIn UI but serves as a placeholder for blank fields, enabling consistent processing and data quality validation.
CluedIn Expression Language (C.E.L.)
CluedIn Expression Language (C.E.L.) is a language used to work with and manipulate your data in CluedIn.
Variables
-
cell – the current cell.
-
value – the current cell’s value; this is a shortcut for ‘cell.value’.
-
row – the current row; it has the index and cells.
-
cells – the cells of the current row. This is a shortcut for ‘row.cells’. A particular cell can be retrieved with
cells.<columnName>if the<column name>is a single word or withcells["<column name>]otherwise. -
column – access to properties of the column (for example, type, name).
Operators
C.E.L. supports the following logical operators:
-
and(&&)return a && b; -
or(||)return a || b; -
not(!)return !a;
String
Case
camelCase
Converts the value to camel case.
camelCase('bird flight');
// => 'birdFlight'
camelCase('BirdFlight');
// => 'birdFlight'
camelCase('-BIRD-FLIGHT-');
// => 'birdFlight'
capitalize
Converts the first character of the value to uppercase. If restToLower is true, convert the rest of value to lowercase.
capitalize('apple');
// => 'Apple'
capitalize('aPPle', true);
// => 'Apple'
decapitalize
Converts the first character of value to lowercase.
decapitalize('Sun');
// => 'sun'
decapitalize('moon');
// => 'moon'
kebabCase
Converts the value to kebab case, also called spinal case or lisp case, where each word is in lowercase and separated with a dash character (-).
kebabCase('goodbye blue sky');
// => 'goodbye-blue-sky'
kebabCase('GoodbyeBlueSky');
// => 'goodbye-blue-sky'
kebabCase('-Goodbye-Blue-Sky-');
// => 'goodbye-blue-sky'
lowerCase
Converts the value to lowercase.
lowerCase('Green');
// => 'green'
lowerCase('BLUE');
// => 'blue'
snakeCase
Converts the value to snake case, where each word is in lowercase and separated with an underscore character (_).
snakeCase('learning to fly');
// => 'learning_to_fly'
snakeCase('LearningToFly');
// => 'learning_to_fly'
snakeCase('-Learning-To-Fly-');
// => 'learning_to_fly'
swapCase
Converts the uppercase alpha characters of a value to lowercase and lowercase characters to uppercase.
swapCase('League of Shadows');
// => 'lEAGUE OF sHADOWS'
swapCase('2 Bees');
// => '2 bEES'
upperCase
Converts the value to uppercase.
upperCase('school');
// => 'SCHOOL'
slugify
Slugifies the value. Cleans the value by replacing diacritics with corresponding Latin characters.
slugify('Italian cappuccino drink');
// => 'italian-cappuccino-drink'
slugify('caffé latté');
// => 'caffe-latte'
slugify('хорошая погода');
// => 'horoshaya-pogoda'
Manipulation
insert
Inserts a string toInsert into value at specified position.
insert('ct', 'a', 1);
// => 'cat'
insert('sunny', ' day', 5);
// => 'sunny day'
trim
Removes whitespaces from left and right sides of the value.
trim(' Mother nature ');
// => 'Mother nature'
trim('--Earth--', '-');
// => 'Earth'
trimLeft
Removes whitespaces from the left side of the value.
trimLeft(' Starship Troopers');
// => 'Starship Troopers'
trimLeft('***Mobile Infantry', '*');
// => 'Mobile Infantry'
trimRight
Removes whitespaces from the right side of the value.
trimRight('the fire rises ');
// => 'the fire rises'
trimRight('do you feel in charge?!!!', '!');
// => 'do you feel in charge?'
latinise
Latinises the value by removing diacritic characters.
latinise('cafe\u0301'); // or 'café'
// => 'cafe'
latinise('août décembre');
// => 'aout decembre'
latinise('как прекрасен этот мир');
// => 'kak prekrasen etot mir'
pad
Pads value to a new length.
pad('dog', 5);
// => ' dog '
pad('bird', 6, '-');
// => '-bird-'
pad('cat', 6, '-=');
// => '-cat-='
padLeft
Pads value from left to a new length.
padLeft('dog', 5);
// => ' dog'
padLeft('bird', 6, '-');
// => '--bird'
padLeft('cat', 6, '-=');
// => '-=-cat'
padRight
Pads value from right to a new length.
padRight('dog', 5);
// => 'dog '
padRight('bird', 6, '-');
// => 'bird--'
padRight('cat', 6, '-=');
// => 'cat-=-'
repeat
Repeats the value a number of times.
repeat('w', 3);
// => 'www'
repeat('world', 0);
// => ''
replace
Replaces the matches of pattern with replacement.
replace('swan', 'wa', 'u');
// => 'sun'
replace('domestic duck', /domestic\s/, '');
// => 'duck'
replace('nice duck', /(nice)(duck)/, (match, nice, duck) => (
'the ' + duck + ' is ' + nice;
));
// => 'the duck is nice'
replaceAll
Replaces all matches of pattern with replacement.
replaceAll('good morning', 'o', '*');
// => 'g**d m*rning'
replaceAll('evening', /n/, 's');
// => 'evesisg'
reverse
Reverses the value.
reverse('winter');
// => 'retniw'
splice
Changes value by deleting deleteCount of characters starting at the position start. Places a new string toAdd instead of deleted characters.
splice('new year', 0, 4);
// => 'year'
splice('new year', 0, 3, 'happy');
// => 'happy year'
splice('new year', -4, 4, 'day');
// => 'new day'
Chain
stringChain
Creates a stringChain object that wraps value, enabling explicit chain sequences. Use value() to unwrap the result.
stringChain('Back to School')
.lowerCase()
.words()
.value()
// => ['back', 'to', 'school']
Chop
charAt
Access a character from a value at specified position.
charAt('helicopter', 0);
// => 'h'
charAt('helicopter', 1);
// => 'e'
first
Extracts the first length characters from a value.
first('helicopter');
// => 'h'
first('vehicle', 2);
// => 've'
first('car', 5);
// => 'car'
last
Extracts the last length characters from a value.
last('helicopter');
// => 'r'
last('vehicle', 2);
// => 'le'
last('car', 5);
// => 'car'
prune
Truncates a value to a new length and does not break the words. Guarantees that the truncated string is no longer than the specified length.
prune('Once upon a time', 7);
// => 'Once...'
prune('Good day, Little Red Riding Hood', 16, ' (more)');
// => 'Good day (more)'
prune('Once upon', 10);
// => 'Once upon'
slice
Extracts a string from value from start position up to end position. The character at the end position is not included.
slice('miami', 1);
// => 'iami'
slice('florida', -4);
// => 'rida'
slice('florida', 1, 4);
// => "lor"
substr
Extracts a string from a value from start position a number of length characters.
substr('infinite loop', 9);
// => 'loop'
substr('dreams', 2, 2);
// => 'ea'
truncate
Truncates a value to a new length.
truncate('Once upon a time', 7);
// => 'Once...'
truncate('Good day, Little Red Riding Hood', 14, ' (...)');
// => 'Good day (...)'
truncate('Once upon', 10);
// => 'Once upon'
count
Counts the characters in a value.
count('rain');
// => 4
split
split('rage against the dying of the light', ' ');
// => ['rage', 'against', 'the', 'dying', 'of', 'the', 'light']
split('the dying of the light', /\s/, 3);
// => ['the', 'dying', 'of']
Math
Construction
mathChain
Wrap any value in a chain, allowing to perform chained operations on the value.
mathChain(3)
.add(4)
.subtract(2)
.done() // 5
Arithmetic
add
Add two or more values, x + y.
add(2, 3) // returns number 5
add(2, 3, 4) // returns number 9
round
Round a value towards the nearest integer.
round(3.2) // returns number 3
round(3.8) // returns number 4
round(-4.2) // returns number -4
round(-4.7) // returns number -5
round(pi, 3) // returns number 3.142
round(123.45678, 2) // returns number 123.46
log
Calculate the logarithm of a value.
log(3.5) // returns 1.252762968495368
exp(log(2.4)) // returns 2.4
pow(10, 4) // returns 10000
log(10000, 10) // returns 4
log(10000) / log(10) // returns 4
log(1024, 2) // returns 10
pow(2, 10) // returns 1024
multiply
Multiply two or more values, x * y.
multiply(4, 5.2) // returns number 20.8
multiply(2, 3, 4) // returns number 24
subtract
Subtract two values, x - y. For matrices, the function is evaluated element-wise.
subtract(5.3, 2) // returns number 3.3
divide
Divide two values, x / y. To divide matrices, x is multiplied with the inverse of y: x * inv(y).
divide(2, 3) // returns number 0.6666666666666666
abs
Calculate the absolute value of a number.
abs(3.5) // returns number 3.5
abs(-4.2) // returns number 4.2
abs([3, -5, -1, 0, 2]) // returns Array [3, 5, 1, 0, 2]
sqrt
Calculate the square root of a value.
sqrt(25) // returns 5
square(5) // returns 25
sqrt(-4) // returns Complex 2i
square
Compute the square of a value, x * x.
square(2) // returns number 4
square(3) // returns number 9
pow(3, 2) // returns number 9
multiply(3, 3) // returns number 9
square([1, 2, 3, 4]) // returns Array [1, 4, 9, 16]
pow
Calculates the power of x to y, x ^ y.
pow(2, 3) // returns number 8
const b = [[1, 2], [4, 3]]
pow(b, 2) // returns Array [[9, 8], [16, 17]]
ceil
Round a value towards plus infinity. If x is complex, both real and imaginary parts are rounded towards plus infinity.
ceil(3.2) // returns number 4
ceil(3.8) // returns number 4
ceil(-4.2) // returns number -4
ceil(-4.7) // returns number -4
ceil([3.2, 3.8, -4.7]) // returns Array [4, 4, -4]
factorial
Factorial only supports an integer value as an argument. For matrices, the function is evaluated element-wise.
factorial(5) // returns 120
factorial(3) // returns 6
gcd
Calculate the greatest common divisor for two or more values or arrays.
gcd(8, 12) // returns 4
gcd(-4, 6) // returns 2
gcd(25, 15, -10) // returns 5
gcd([8, -4], [12, 6]) // returns [4, 2]
Statistics
min
Compute the minimum value of a matrix or a list of values.
max(2, 1, 4, 3) // returns 4
max([2, 1, 4, 3]) // returns 4
// maximum over a specified dimension (zero-based)
max([[2, 5], [4, 3], [1, 7]], 0) // returns [4, 7]
max([[2, 5], [4, 3]], [1, 7], 1) // returns [5, 4, 7]
max(2.7, 7.1, -4.5, 2.0, 4.1) // returns 7.1
min(2.7, 7.1, -4.5, 2.0, 4.1) // returns -4.5
max
Compute the maximum value of a matrix or a list with values. In case of a multi-dimensional array, the maximum of the flattened array will be calculated. When dim is provided, the maximum over the selected dimension will be calculated. Parameter dim is zero-based.
max(2, 1, 4, 3) // returns 4
max([2, 1, 4, 3]) // returns 4
// maximum over a specified dimension (zero-based)
max([[2, 5], [4, 3], [1, 7]], 0) // returns [4, 7]
max([[2, 5], [4, 3]], [1, 7], 1) // returns [5, 4, 7]
max(2.7, 7.1, -4.5, 2.0, 4.1) // returns 7.1
min(2.7, 7.1, -4.5, 2.0, 4.1) // returns -4.5
Trigonometry functions
cos
Calculate the cosine of a value.
cos(2) // returns number -0.4161468365471422
cos(pi / 4) // returns number 0.7071067811865475
cos(unit(180, 'deg')) // returns number -1
cos(unit(60, 'deg')) // returns number 0.5
const angle = 0.2
pow(sin(angle), 2) + pow(cos(angle), 2) // returns number ~1
cosh
Calculate the hyperbolic cosine of a value, defined as cosh(x) = 1/2 * (exp(x) + exp(-x)).
cosh(0.5) // returns number 1.1276259652063807
sin
Calculate the inverse sine of a value.
asin(0.5) // returns number 0.5235987755982989
asin(sin(1.5)) // returns number ~1.5
asin(2) // returns Complex 1.5707963267948966 -1.3169578969248166 i
sinh
Calculate the hyperbolic sine of a value, defined as sinh(x) = 1/2 * (exp(x) - exp(-x)).
sinh(0.5) // returns number 0.5210953054937474
tan
Calculate the tangent of a value.
tan(0.5) // returns number 0.5463024898437905
sin(0.5) / cos(0.5) // returns number 0.5463024898437905
tan(pi / 4) // returns number 1
tan(unit(45, 'deg')) // returns number 1
tanh
Calculate the hyperbolic tangent of a value, defined as tanh(x) = (exp(2 * x) - 1) / (exp(2 * x) + 1).
// tanh(x) = sinh(x) / cosh(x) = 1 / coth(x)
tanh(0.5) // returns 0.46211715726000974
sinh(0.5) / cosh(0.5) // returns 0.46211715726000974
1 / coth(0.5) // returns 0.46211715726000974
Constants
e
Euler’s number, the base of the natural logarithm.
e
pi
The number pi is a mathematical constant that is the ratio of a circle’s circumference to its diameter.
pi
phi
Phi is the golden ratio. Two quantities are in the golden ratio if their ratio is the same as the ratio of their sum to the larger of the two quantities. Phi is defined as (1 + sqrt(5)) / 2.
phi
Utils
isInteger
Test whether a value is an integer number.
isInteger(2) // returns true
isInteger(0) // returns true
isInteger(0.5) // returns false
isInteger(bignumber(500)) // returns true
isInteger(fraction(4)) // returns true
isInteger('3') // returns true
isInteger([3, 0.5, -2]) // returns [true, false, true]
isNaN
Test whether a value is NaN (not a number). The function supports such types as number, BigNumber, Fraction, Unit, and Complex.
isNaN(3) // returns false
isNaN(NaN) // returns true
isNaN(0) // returns false
isNaN(bignumber(NaN)) // returns true
isNaN(bignumber(0)) // returns false
isNaN(fraction(-2, 5)) // returns false
isNaN('-2') // returns false
isNaN([2, 0, -3, NaN]') // returns [false, false, false, true]
isNegative
Test whether a value is negative: smaller than zero. The function supports such types as number, BigNumber, Fraction, and Unit.
isNegative(3) // returns false
isNegative(-2) // returns true
isNegative(0) // returns false
isNegative(-0) // returns false
isNegative(bignumber(2)) // returns false
isNegative(fraction(-2, 5)) // returns true
isNegative('-2') // returns true
isNegative([2, 0, -3]') // returns [false, false, true]
isNumeric
Test whether a value is a numeric value.
isNumeric(2) // returns true
isNumeric('2') // returns true
hasNumericValue('2') // returns true
isNumeric(0) // returns true
isNumeric(bignumber(500)) // returns true
isNumeric(fraction(4)) // returns true
isNumeric([2.3, 'foo', false]) // returns [true, false, true]
isPositive
Test whether a value is positive: larger than zero. The function supports such types as number, BigNumber, Fraction, and Unit.
isPositive(3) // returns true
isPositive(-2) // returns false
isPositive(0) // returns false
isPositive(-0) // returns false
isPositive(0.5) // returns true
isPositive(bignumber(2)) // returns true
isPositive(fraction(-2, 5)) // returns false
isPositive(fraction(1,3)) // returns false
isPositive('2') // returns true
isPositive([2, 0, -3]) // returns [true, false, false]
isPrime
Test whether a value is prime: has no divisors other than itself and one.
isPrime(3) // returns true
isPrime(-2) // returns false
isPrime(0) // returns false
isPrime(-0) // returns false
isPrime(0.5) // returns false
isPrime('2') // returns true
isPrime([2, 17, 100]) // returns [true, true, false]
isZero
Test whether a value is zero.
isZero(0) // returns true
isZero(2) // returns false
isZero(0.5) // returns false
isZero(bignumber(0)) // returns true
isZero(fraction(0)) // returns true
isZero(fraction(1,3)) // returns false
isZero('0') // returns true
isZero('2') // returns false
isZero([2, 0, -3]') // returns [false, true, false]