CluedIn in your data architecture
On this page
- High-level data architecture
- Fabric use case
- Databricks use case
- Azure Data Factory use case
- Synapse use case
In this article, we’ll explain the global way CluedIn fits into your organization’s data architecture.
High-level data architecture
To begin with, CluedIn can connect with a variety of different systems and services, both to receive source data and to export golden records. The following diagram illustrates the most common source systems that can send data to CluedIn’s ingestion endpoints and the most common export systems that can receive golden records from CluedIn.
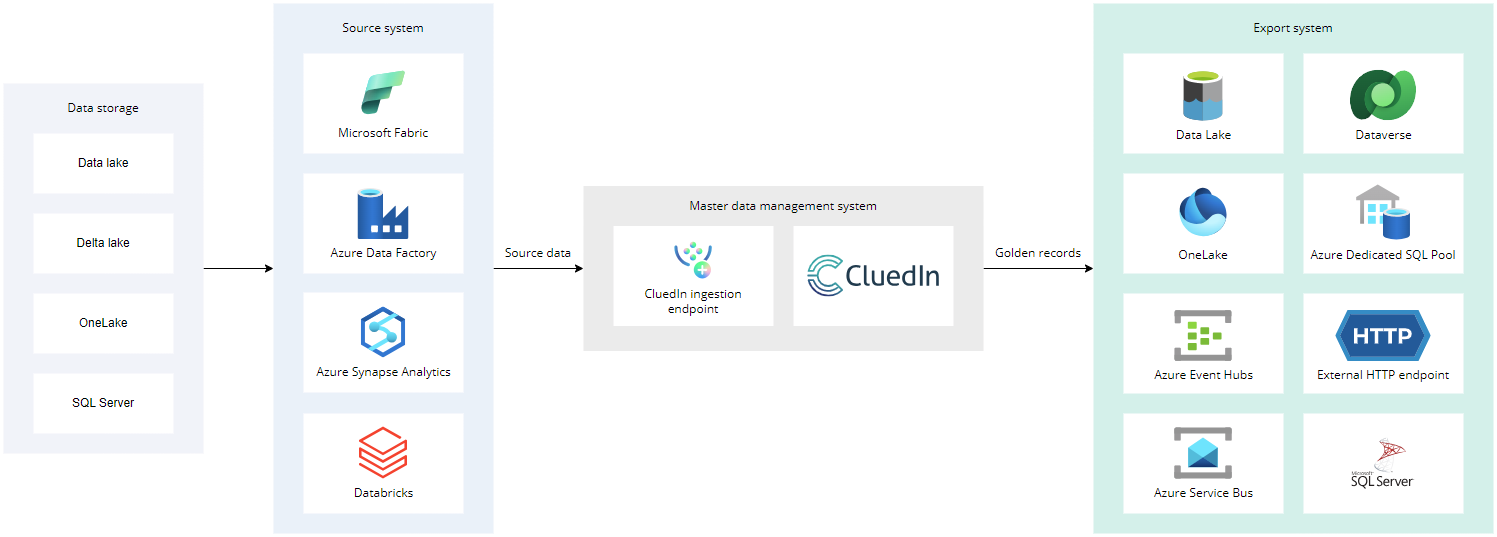
The most common source systems include:
-
Microsoft Fabric – an end-to-end analytics and data platform designed for enterprises that require a unified solution. It encompasses data movement, processing, ingestion, transformation, real-time event routing, and report building.
-
Azure Data Factory – Azure’s cloud ETL service for scale-out serverless data integration and data transformation. It offers a code-free UI for intuitive authoring and single-pane-of-glass monitoring and management.
-
Azure Synapse Analytics – a limitless analytics service that brings together enterprise data warehousing and Big Data analytics. It supports both SQL-based and Spark-based analytics, enabling a wide range of data processing and analysis tasks.
-
Databricks – a unified analytics platform that integrates with cloud data storage, allowing for efficient data processing and management. It provides a web interface where you can create a notebook that connects to Spark, allowing you to perform data transformation tasks. From the data architecture standpoint, the purpose of Databricks is similar to Microsoft Fabric since both platforms provide robust tools for managing and processing large volumes of data.
These source systems usually retrieve data from data storages—data lake, delta lake, OneLake, or SQL Server. Then, they send the source data to CluedIn using an ingestion endpoint.
Regardless of the source system, the pipelines for sending the source data to the ingestion endpoint in CluedIn are similar.
Your data architecture might also include additional elements such as:
-
Data storage services:
-
Data Lake – a storage repository that holds a large amount of data in its native, raw format.
-
OneLake – a single, unified, logical data lake for the whole organization. OneLake comes automatically with every Microsoft Fabric tenant with no infrastructure to manage.
Essentially, the purpose of Data Lake and OneLake is similar as they both serve as centralized repositories for storing large volumes of data. However, OneLake is specifically designed for integration within the Microsoft Fabric ecosystem.
-
-
Data processing services:
-
Apache Spark – a distributed processing system designed for big data workloads. It provides a multi-language analytics engine for large-scale data engineering and data processing. Spark is integrated into Microsoft Fabric, which allows for fast data processing using notebooks. Spark can read data both from Data Lake and OneLake.
-
SQL Pool – provides scalable and high-performance SQL-based analytics capabilities. It integrates seamlessly Fabric Warehouse to enable comprehensive data processing and analytics workflows.
-
-
Subsystems in Fabric:
-
Lakehouse – a data architecture platform for storing, managing, and analyzing structured and unstructured data in a single location. You can read the data stored in the Lakehouse through Spark.
-
Warehouse – a next-generation data warehousing solution within Microsoft Fabric designed to provide high performance and scalability while simplifying configuration and management. A Warehouse in Fabric is essentially a SQL Pool.
-
These elements will be illustrated further down when we look at the use cases for each source system.
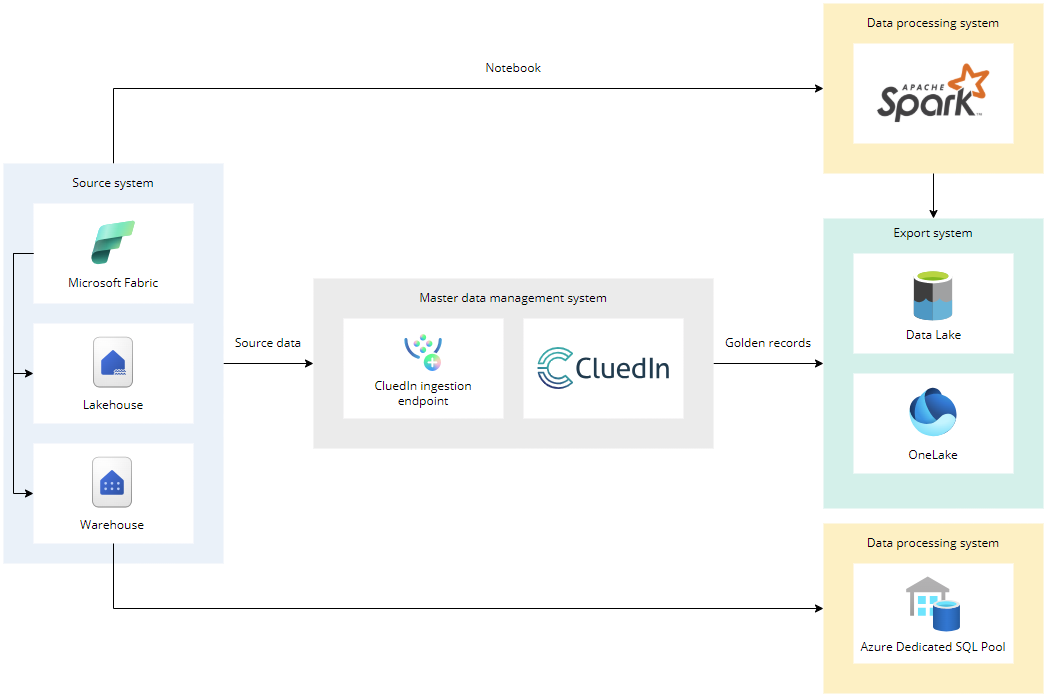
Fabric use case
Microsoft Fabric can read data from data storages with the help of notebooks and send that data into CluedIn. Also, Fabric can read data from CluedIn and send it to data storages.
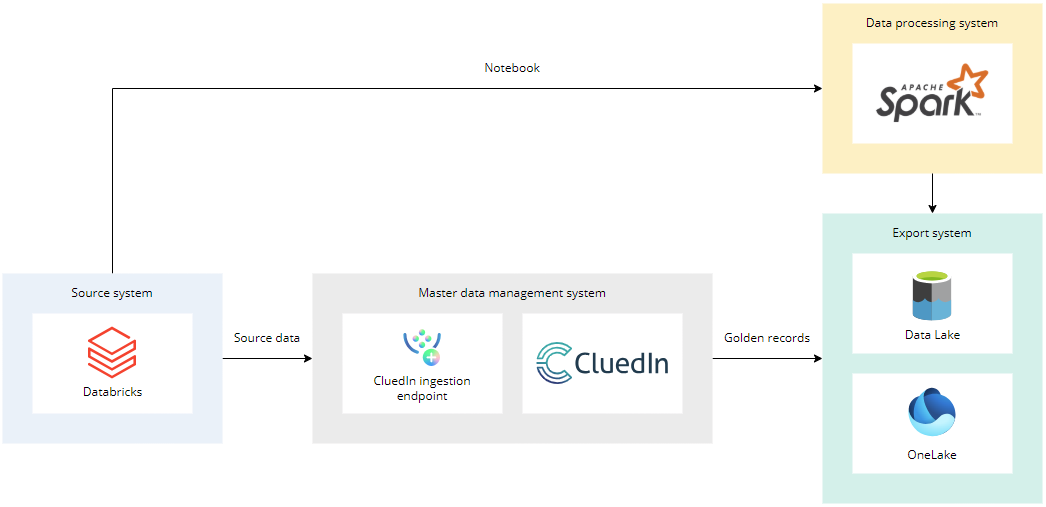
Databricks use case
Databricks can read data from data storages with the help of notebooks and send that data into CluedIn. Also, Databricks can read data from CluedIn and send it to data storages.
Azure Data Factory use case
Azure Data Factory can operate as a standalone product, being a source system for CluedIn. It also can be a part of Microsoft Fabric, providing data ingestion pipelines.
Azure Data Factory can read data from data storages and send that data into CluedIn. Also, Azure Data Factory can read data from CluedIn and send it to data storages.

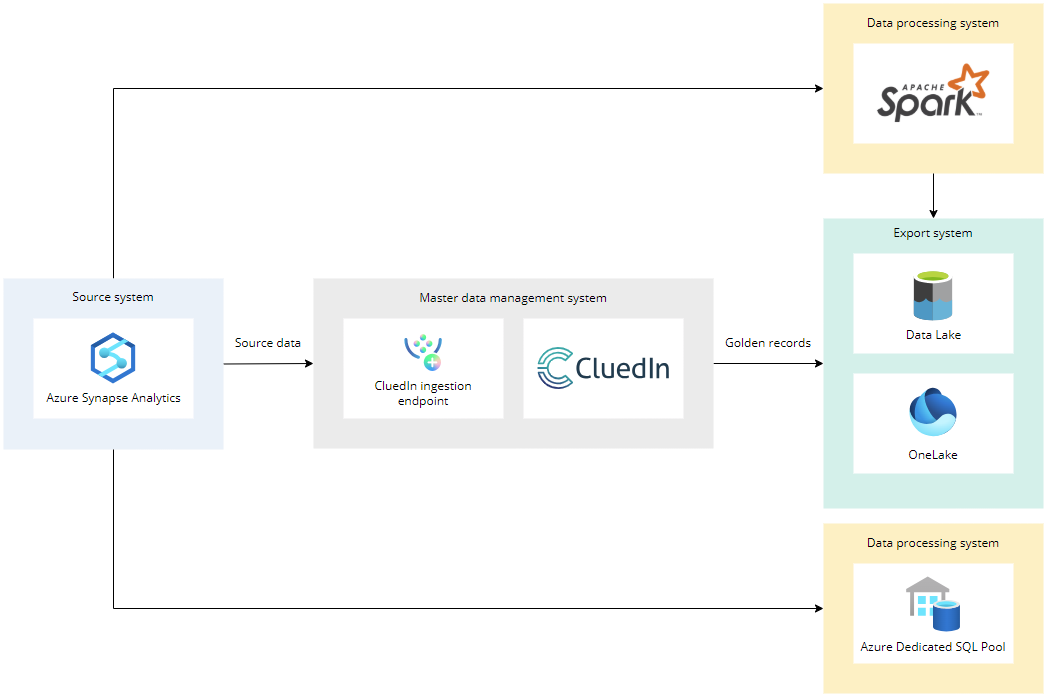
Synapse use case
Azure Synapse Analytics can read data from data storages with the help of Spark and SQL Pool and send that data to CluedIn.