Roles
On this page
- Default roles
- Understanding roles, claims, and access levels
- View role details
- Supported access levels
- Managing overlapping roles
In this article, you will learn about claims and access levels, which are the main concepts that define roles.
Roles are used to grant permissions to users to perform specific actions in CluedIn. These permissions are only granted to the modules within the platform, not to the data. For information on how to restrict access to data, see Data access.
Default roles
All roles are listed in Administration > Roles. The following table provides a list of default CluedIn roles. In the Access status column, you can download a file with details of the default role’s access to the features in CluedIn. However, you can change the configuration of the role and extend its access to features according to your needs.
| Role name | Description | Access status |
|---|---|---|
| DataArchitect | Responsible for designing an organization’s enterprise data strategy. | Download |
| DataCompliance | Responsible for daily operations around data compliance. | Download |
| DataComplianceAdministrator | Responsible for approving changes made by users with the DataCompliance role. | Download |
| DataGovernance | Responsible for monitoring and maintaining data quality. | Download |
| DataGovernanceAdministrator | Responsible for approving changes made by the users with the DataGovernance role. | Download |
| DataSteward | Responsible for cleaning data using the Clean and Prepare modules. | Download |
| DataStewardAdministrator | Responsible for approving changes made by the users with the DataSteward role. | Download |
| DeduplicationAdministrator | Responsible for creating and maintaining deduplication projects and merging the results back into the system. | Download |
| DeduplicationReviewer | Responsible for reviewing deduplication project results and approving groupings. | Download |
| Guest | User with minimal, read-only permissions. | Download |
| OrganizationAdmin | Administrator within the organization. | Download |
| OrganizationUser | User within the organization who can view all modules as read-only. | Download |
| ReportManager | User who can generate reports for compliance matters such as breach, subject request, and retention. | Download |
| User | User who can view all modules as read-only. | Download |
Understanding roles, claims, and access levels
A role acts as a container for two key components:
-
Claims – Specific features or operations that can be performed in CluedIn. Most of the time, the name of the claim is the same as the name of the module in CluedIn. Learn more about claims in a dedicated article.
-
Access levels – Indicate the type of activity that can be performed with the claim.
To get acquainted with the required claims and access levels for all actions in CluedIn, download this file.
View role details
-
On the navigation pane, go to Administration > Roles.
-
Select a role to view its claims and access levels.
You can view the following information:
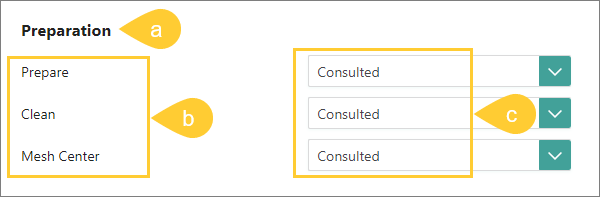
-
The name of the section in CluedIn (a).
-
Claims within that section (b).
-
Access levels (c) to each claim.
Each role contains the same list of claims, but different access levels. We recommend that you familiarize yourself with the default CluedIn roles, so that you know which role to assign to users in your organization. If the default configuration is not suitable for you, you can change the access levels in the default roles or create your own roles.
-
Supported access levels
In CluedIn, the following access levels are used:
- None – No access to the claim.
- Informed – Read-only access to the claim. The user will be able to view all information within the claim, but will not be able to add, edit, or delete items within the claim.
- Consulted – Read and write access to the claim. The user will be able to add, edit, or delete items within the claim.
The Responsible and Accountable access levels are reserved for upcoming versions. Currently, the activities represented by these access levels are the same as in the Consulted access level.
Managing overlapping roles
All authorized users have a list of claims and access levels applied to them. If a user has multiple roles with different claim access levels, then the higher access level will be applied to the user.