Azure SQL migration
On this page
- Overview
- Azure SQL Server Creation
- Migrating Existing SQL to Azure SQL
- Helm Upgrade (Post-Migration)
- Infrastructure Changes & Costs
This document outlines the process of provisioning Azure SQL infrastructure and migrating data from an existing in-cluster SQL database to Azure SQL.
The process is split into two parts:
- Azure SQL Server Creation
- Migrating Existing SQL to Azure SQL
- Infrastructure Changes & Costs
Overview
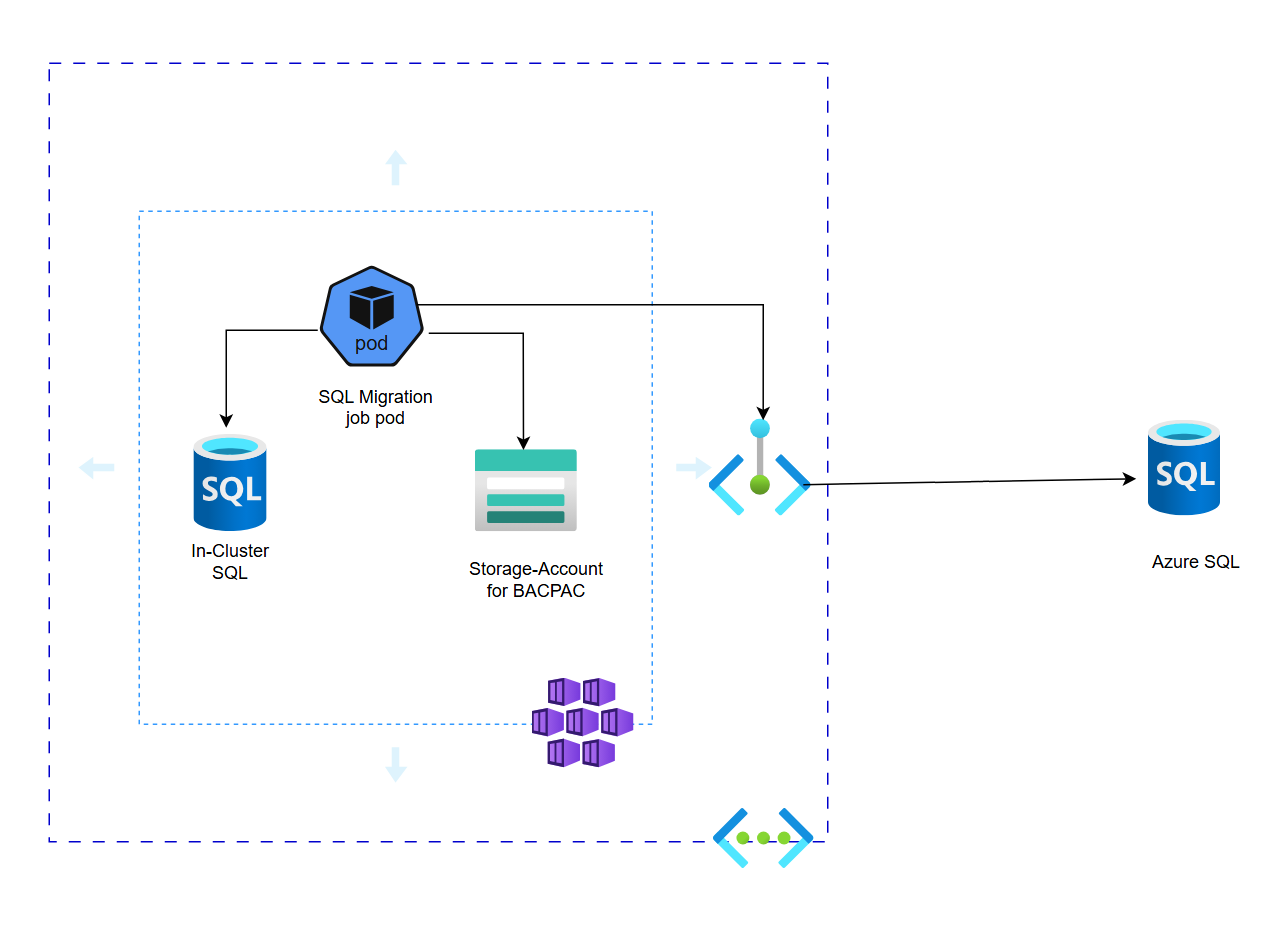
This migration is designed to run entirely within the AKS cluster, leveraging an in-cluster job that:
- Connects to both the existing in-cluster SQL instance and the target Azure SQL Database
- Exports the data from the in-cluster SQL as a BACPAC file
- Uploads the BACPAC file to an Azure Storage Account
- Imports the BACPAC into the Azure SQL database
This approach ensures secure, seamless, and auditable data migration without requiring any manual data export/import actions outside of the cluster.
Azure SQL Server Creation
Pre-requisites:
- Ensure the current instance is upgraded with 4.6.0 (Egret)
- Ensure the following Azure role assignments:
- Contributor
- Network Contributor
- Private DNS Zone Contributor
- Get the Bicep template from
Global Ops
Steps
- Prepare Input Parameters:
- Update the Vnet & subnet IDs
- Update the Azure SQL username & password
- Change the specs if you want to choose different from default
-
Run Bicep Template:
Deploys the following components:
- Azure SQL Server
- Elastic Pool (optional)
- CluedIn Databases
- Private endpoint
- Private DNS zone
-
Validation Checklist:
- SQL server successfully provisioned
- Private endpoint connected and DNS resolving
- SQL server reachable via Azure Data Studio or sqlcmd from within the VNet
Migrating Existing SQL to Azure SQL
Pre-requisites
-
Scale Down Data Processing:
kubectl scale deploy cluedin-server cluedin-server-processing cluedin-datasource-processing cluedin-datasource-submitter cluedin-gql cluedin-ui -n cluedin --replicas=0 --timeout 5m -
Patch Persistent Volume:
Ensure in-cluster SQL disk isn’t deleted on PV release:
kubectl patch pv <pv-name> -p '{"spec":{"persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy":"Retain"}}' -
Check the existing in-cluster SQL DB size to estimate migration time:
kubectl exec -it <cluedin-sql-pod-name> -n cluedin -- /opt/mssql-tools/bin/sqlcmd \ -S localhost -U sa -P <SA_PASSWORD> \ -Q "SET NOCOUNT ON; CREATE TABLE #Space (DBName SYSNAME, DataSize NVARCHAR(50), LogSize NVARCHAR(50)); EXEC sp_MSforeachdb 'USE [?]; INSERT INTO #Space SELECT DB_NAME(), (SELECT SUM(size)*8/1024 FROM sys.database_files WHERE type_desc=''ROWS''), (SELECT SUM(size)*8/1024 FROM sys.database_files WHERE type_desc=''LOG'');'; SELECT DBName AS [Database], DataSize AS [Data(MB)], LogSize AS [Log(MB)] FROM #Space; DROP TABLE #Space;"If any DB is larger than 30GB, consider increasing the individual DB storage size on Azure SQL. All the DBs are created with 32GB by default.
Migration Steps
-
Get the migration script & update SQL Secrets:
Edit your Kubernetes YAML to include the new Azure SQL host, username, and password. And update the in-cluster SQL secret
-
Apply Migration Manifest:
kubectl apply -f cluedin-sql-migration.yaml -n cluedin -
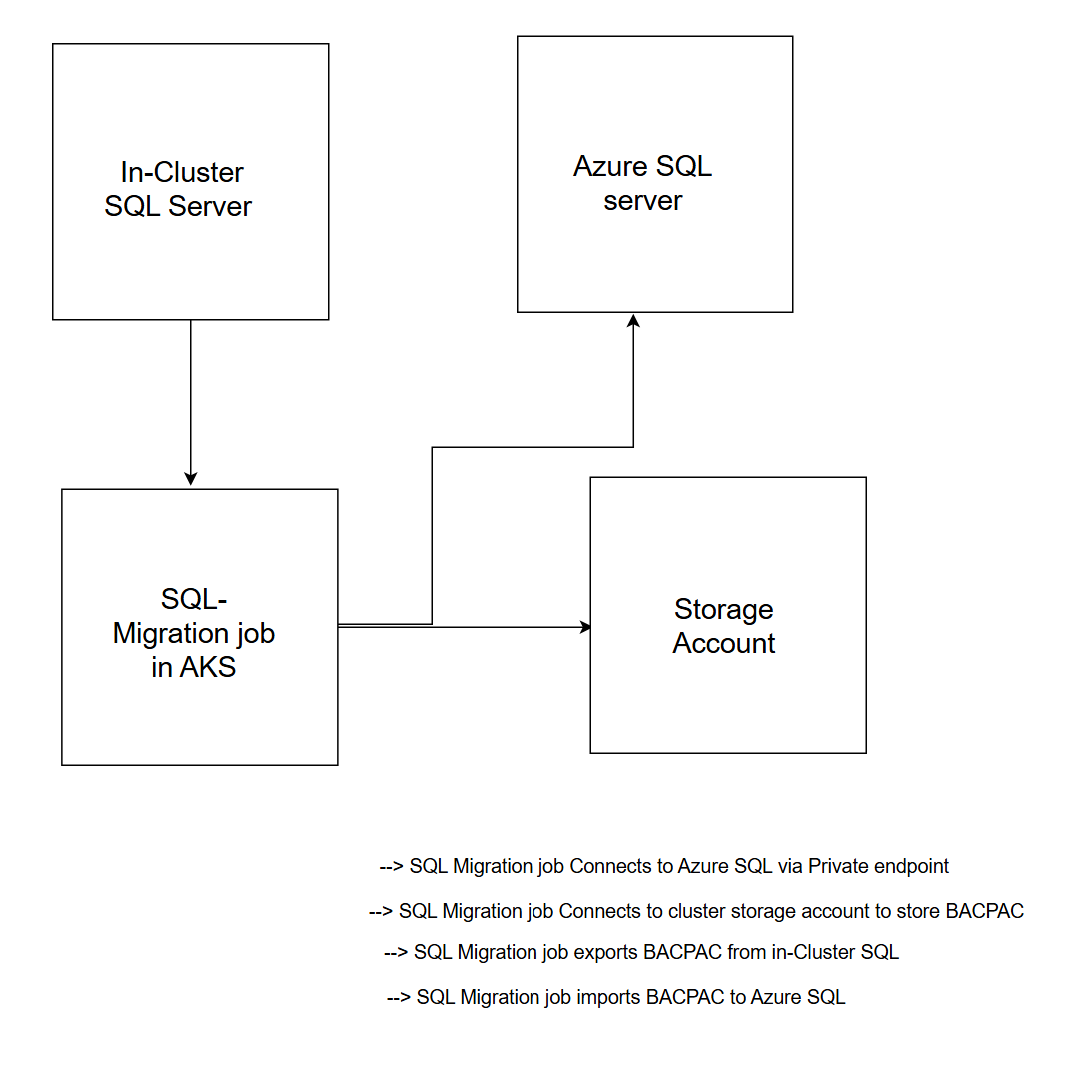
This job will:
- Connect to the in-cluster SQL
- Export DB to BACPAC
- Upload BACPAC to Azure Storage
- Import BACPAC into Azure SQL
- Monitor Job Logs:
kubectl logs job/<sql-migration-job-name> -n cluedin - Verify Data in Azure SQL:
- Connect using Azure Data Studio or sqlcmd
- Validate that table counts and data match the original in-cluster database
Helm Upgrade (Post-Migration)
- Backup Existing in-cluster SQL Secret:
kubectl get secret cluedin-sqlserver-secret -n cluedin -o yaml > sql-secret-backup.yaml -
Update Helm Values:
Backup the current helm values and rename it to new values.yaml and insert the Azure SQL connection values into the new values.yaml.
application: sqlserver: host: <AZURE_SQL_SERVER>.database.windows.net isExternal: true connectionOptions: timeout: 15 encrypt: true extraParameters: "Max Pool Size=200;Pooling=True;" users: sa: username: <AZURE_SQL_ADMIN_USERNAME> passwordSecretName: cluedin-sqlserver-secret cluedincontroller: hosts: sqlserver: host: <AZURE_SQL_SERVER>.database.windows.net connectionOptions: encrypt: true extraParameters: Max Pool Size=200;Pooling=True; timeout: 15 isExternal: true users: sa: passwordSecretName: cluedin-sqlserver-secret username: <AZURE_SQL_ADMIN_USERNAME> infrastructure: mssql: enabled: false platform: extraSecrets: cluedin-sqlserver-secret: sapassword: <Azure_SQL_ADMIN_PASSWORD>note: If keyvault is used, update the keyvault secret
cluedin-mssql-sa-passwordwith new Azure SQL password -
Scale down the in-cluster SQL deployment and remove the sql secret cluedin-sqlserver-secret
- Run Helm Upgrade:
helm upgrade -i cluedin-platform -n cluedin cluedin-platform/cluedin-platform --version 2.6.x --values values.yaml --set application.system.runDatabaseJobsOnUpgrade=true - Post-Deployment Checks:
- All pods should be in Running state
- UI should be accessible
- Run sanity tests
Infrastructure Changes & Costs
The switch from an internal MS SQL deployment to Azure SQL impacts the underlying infrastructure and, as a result, the expected costs. The costs outlined below are accurate as of January 2026.
Added / Modified Infrastructure
| Resource | Region | Spec | Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Azure SQL Database | East US | Elastic Pool, SKU: General Purpose, 4 x vCore, 500Gb storage LRS | $737.37 |
| Virtual Machine Scale Sets: Data | East US | D4as v5 | $125.56 |
| Total | $862.93 |
Removed / Modified Infrastructure
| Resource | Region | Spec | Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Managed Disks: MS SQL | East US | Premium SSD, LRS Redundancy, P30 Disk | $540.68 |
| Virtual Machine Scale Sets: Data | East US | D8as v5 | $251.12 |
| Total | $791.80 |
Approximate price difference: $71.13. Note: Prices may vary slightly depending on region and data consumption.