Using Python SDK for Automation
On this page
CluedIn, as a Master Data Management system, encourages users to work with data using a UI and low-code approach. You can do a full data cycle from ingesting data into CluedIn to data modeling, transformation, cleaning, enriching, deduplication, and export without writing a single line of code.
However, there are situations when automation and basic scripting can save the day. Moreover, in the same way as we can free business users from dealing with IT and code, we can free them from repetitive actions in UI when, for example, you implement a CI/CD pipeline between your development, staging, and production instances.
In this article, we will implement basic automation without knowing too much about it beforehand. Let’s start with the fact that CluedIn UI communicates with the server via GraphQL API.
Two GraphQL API endpoints
CluedIn provides two GraphQL API endpoints:
/api/api/graphql– the endpoint used to query data./graphql– the endpoint for UI interactions.
Authentication
CluedIn uses JWT token-based authorization.
There are two kinds of tokens in CluedIn:
-
API tokens – are used to extract or ingest data from and into CluedIn. You can create or copy an API token from Administration > API Tokens.
-
Access tokens – are generated when you log in to CluedIn as a user.
You need an API token to use the /api/api/graphql endpoint.
The /graphql endpoint only accepts access tokens, which means you must log in with your email and password to obtain one.
Exploring GraphQL API
In this article, we explore a use case of automating the actions you usually do in UI with the help of CluedIn GraphQL API and CluedIn Python SDK.
Let’s use a simple example: you want to automate Vocabulary creation. You can do it from the CluedIn UI, but you would prefer an automated approach to synchronize Vocabularies from another place.
The first thing you can do is create a test Vocabulary in a browser and see how the API calls look. You can do it using:
-
(Better) GraphQL Network Inspector.
Let’s try both approaches.
-
Go to the UI and create a test CluedIn Vocabulary while keeping the Network tab open.

Now, when we inspect GraphQL queries, we can see the
createVocabularymutation call.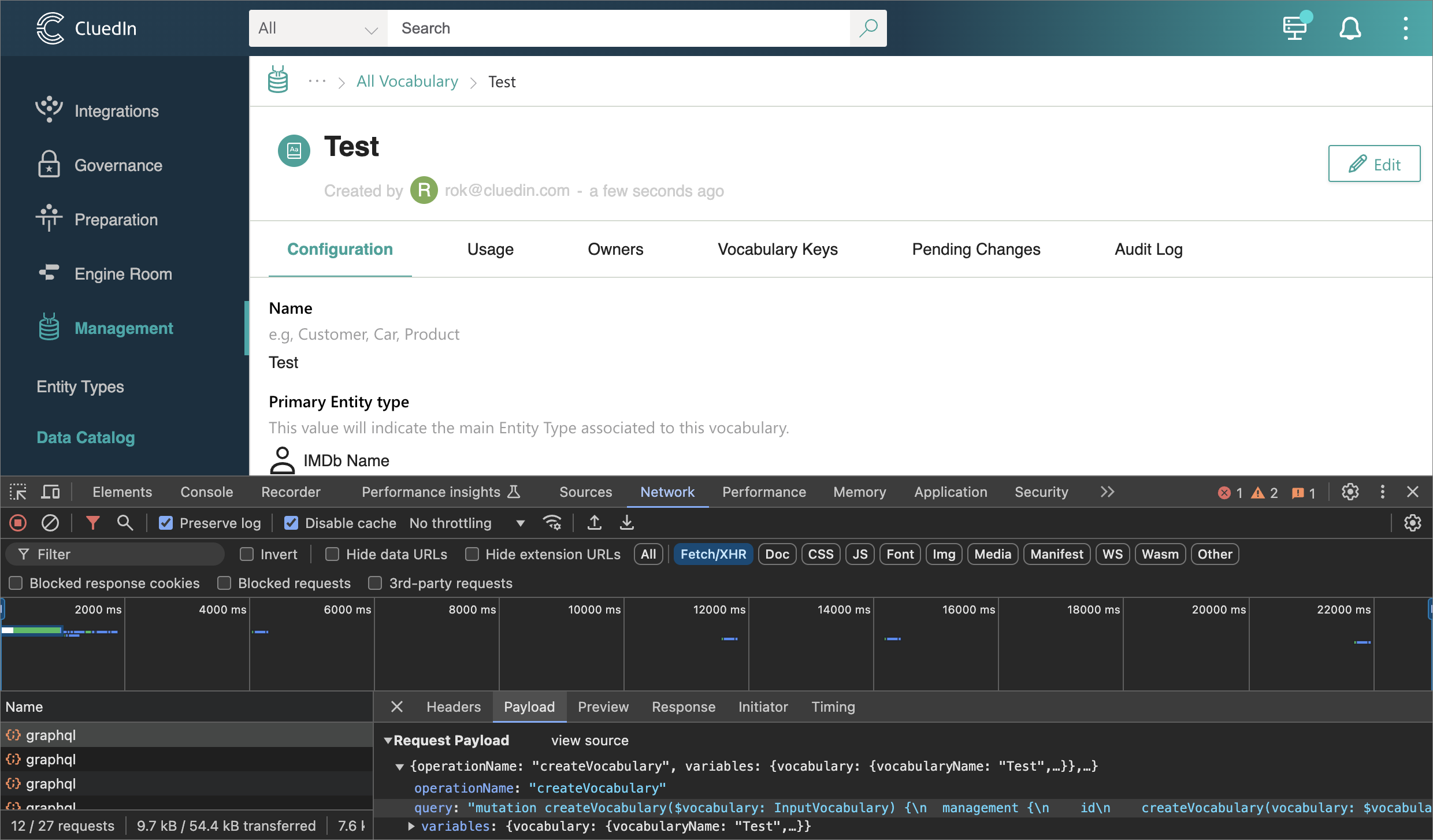
Finding the right call is even easier with GraphQL Network Inspector:
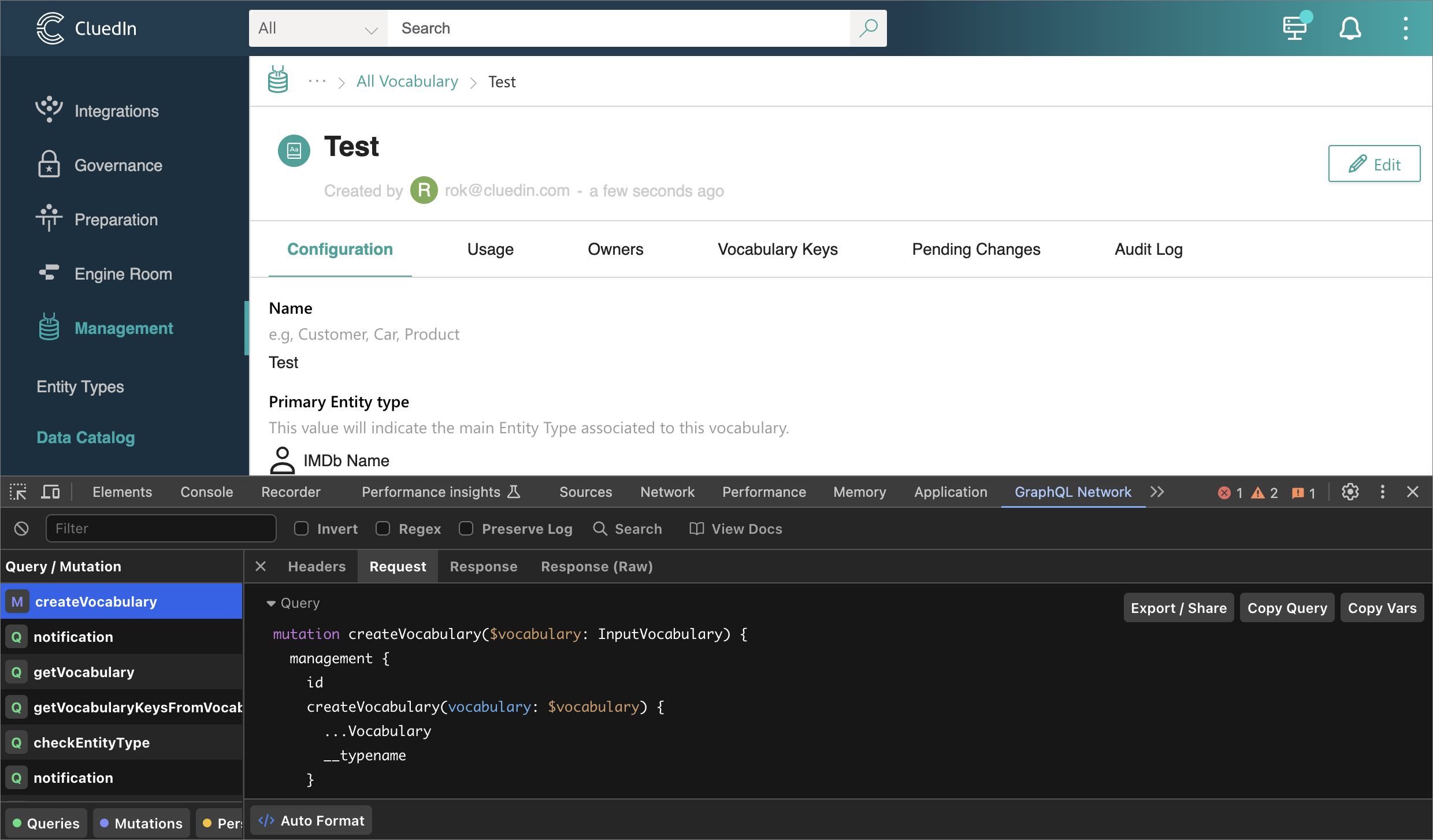
-
Regardless how we found the call, we can now copy the GraphQL query:
mutation createVocabulary($vocabulary: InputVocabulary) { management { id createVocabulary(vocabulary: $vocabulary) { ...Vocabulary __typename } __typename } } fragment Vocabulary on Vocabulary { vocabularyId vocabularyName keyPrefix isCluedInCore entityTypeConfiguration { icon entityType displayName __typename } isDynamic isProvider isActive grouping createdAt providerId description connector { id name about icon __typename } __typename }And the variables:
{ "vocabulary": { "vocabularyName": "Test", "entityTypeConfiguration": { "new": false, "icon": "Profile", "entityType": "/IMDb/Name", "displayName": "IMDb Name" }, "providerId": "", "keyPrefix": "test", "description": "" } }
Python SDK
Now, we can use the CluedIn Python SDK to create a Vocabulary.
-
Create a file with CluedIn credentials. You can also provide them via environment variables:
{ "domain": "172.167.52.102.sslip.io", "org_name": "foobar", "user_email": "admin@foobar.com", "user_password": "mysecretpassword" } -
Install the CluedIn Python SDK:
%pip install cluedin -
Sign in to CluedIn to get the access token:
import cluedin ctx = cluedin.Context.from_json_file('cluedin.json') ctx.get_token() -
The
ctxobject now contains the access token, and we can use it to create a Vocabulary:def create_vocabulary(ctx, name, prefix): query = """ mutation createVocabulary($vocabulary: InputVocabulary) { management { id createVocabulary(vocabulary: $vocabulary) { ...Vocabulary } } } fragment Vocabulary on Vocabulary { vocabularyId vocabularyName keyPrefix entityTypeConfiguration { icon entityType displayName } providerId description } """ variables = { "vocabulary": { "vocabularyName": name, "entityTypeConfiguration": { "new": False, "icon": "Profile", "entityType": "/IMDb/Name", "displayName": "IMDb Name" }, "providerId": "", "keyPrefix": prefix, "description": "" } } return cluedin.gql.org_gql(ctx, query, variables) -
Let’s test vocabulary creation:
print(create_vocabulary(ctx, 'Foo Bar', 'foo.bar'))Output:
{ "data": { "management": { "id": "management", "createVocabulary": { "vocabularyId": "e4528e92-f4ad-406a-aeab-756acc20fd01", "vocabularyName": "Foo Bar", "keyPrefix": "foo.bar", "entityTypeConfiguration": { "icon": "Profile", "entityType": "/IMDb/Name", "displayName": "IMDb Name" }, "providerId": null, "description": "" } } } } -
Check the vocabulary in the UI:

Here are a couple more of examples used on real projects:
- Create missing Vocabularies and keys for a given Entity: ensure_vocab_keys.py.
- Explore a CluedIn Entity’s Data Parts to troubleshoot overmerging: scrutinize_entity.py.